Anatomy of thoracic wall
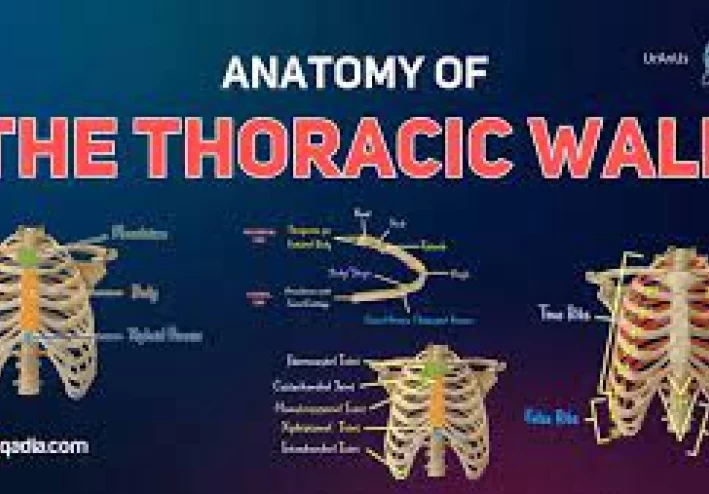
Skeleton of thoracic wall
It’s formed by 12 thoracic vertebrae with intervertebral disc posteriorly, twelve pairs of ribs and associated costal cartilages on each side and the sternum anteriorly. There are three types of bones: thoracic vertebrae, ribs and sternum
Thoracic vertebrae The thoracic spine is the 2nd segment of vertebral column, lie between cervical and lumbar vertebral segments. It is composed of 12 vertebrae. Body: heart-shaped which increases in size when descending to lumbar vertebrae Spinous process : dorsal bony prominence Transverse process: bone-shaped process originating from vertebral arch Upper and lower articular facets: articulation surfaces for adjacent upper and lower vertebrae Costal facets: articulation surfaces for head of rib Vertebral foramen: large opening posterior to body forming spinal canal through which spinal cord passes. Intervertebral foramen: paired foramina (left, right) intended for the exiting nerve roots Ribs The ribs are composed of twelve bones. They articulate posteriorly with the vertebral column and terminate as costal cartilage anteriorly.
Articulations of ribs : the ribs have anterior and posterior articulation. Anterior Ribs 1st:7th ) True ribs ) attach to the sternum. Ribs 8th :10th ( false ribs ) attach to the costal cartilages superiorly. Ribs 11th and 12th (floating ribs) end in the abdominal musculature and don’t have anterior attachment. Posterior The ribs articulate with the thoracic vertebrae forming two joints: Costovertebral joint : Between the head of rib, upper costal facet of corresponding vertebrae, and the lower costal facet of vertebrae above. Costotransverse joint: Between the tubercle of rib, and the transverse costal facet of corresponding vertebrae. Rib Structure There are two types of ribs (atypical and typical) . Typical Ribs The typical rib is composed of a head, neck and body: Head: wedge shaped and has two articular facets. One articulates with corresponding vertebrae and other articulates with vertebrae above
Neck: connects head and body together and doesn’t contain bony prominences. There is rough tubercle where body meets neck, with facet which articulates with transverse process of corresponding vertebrae. Body (shaft) : flat and curved . The internal surface of body has a groove for the neurovascular supply of thorax which protects nerves and vessels from damage Atypical Ribs Ribs 1, 2, 10, 11 and 12 can be described as (atypical) because they have features which are not common to all ribs. Rib 1 is wider and shorter than other ribs. It has only one facet on its head which articulates with its corresponding vertebrae Rib 2 is longer and thinner than rib one. It has a roughened area on its upper surface, where the serratus anterior muscle originates, and normally has two articular facets on head. Rib 10 only has one facet which articulates with its corresponding vertebrae. Ribs 11 and 12 don’t have neck, and only contain one facet, that articulates with their corresponding vertebrae































