

If he’s just getting started, diving into investing can feel like navigating a maze. But with the right beginner-friendly investment strategies, a clear plan, and consistent action, he can set the foundation for long-term financial success. This guide will walk him through how to start investing with little money, covering everything from how to set goals to picking best investments for beginners and building a beginner investment portfolio
1. Why Should a Beginner Invest?
Before he picks his first investment, he should understand why investing matters for someone just starting out.
His money sitting in a standard savings account likely won’t keep up with inflation. In other words: If inflation is 3 % and his savings yield 1 %, his money is effectively losing buying power over time.
Investing gives him a chance to grow wealth over time, rather than just preserving it. As one guide puts it, investing isn’t just for the rich — it is where he can build wealth.
The earlier he starts, the more time compound growth works in his favor. Even small contributions, consistently over years, can add up.
No matter how much or how little money you have, it’s always a good idea to invest as much as you are able to.” — from a beginner’s guide.
Bottom line: He doesn’t need a big lump sum to begin. What matters more is starting, staying consistent, and being patient.
2. Key Terms & Concepts (Basics of Investing for Beginners)
Before jumping into picking investments, he'll benefit from understanding some foundational concepts.
Asset classes and the risk ladder
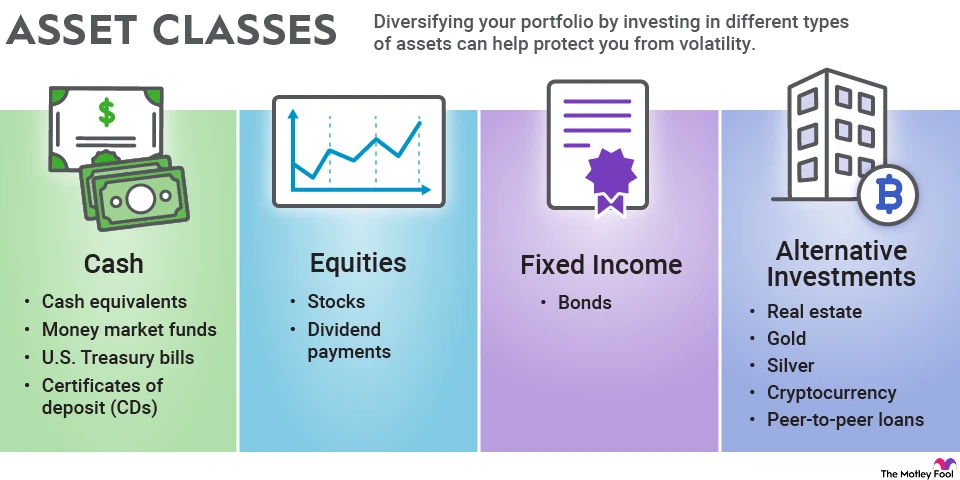

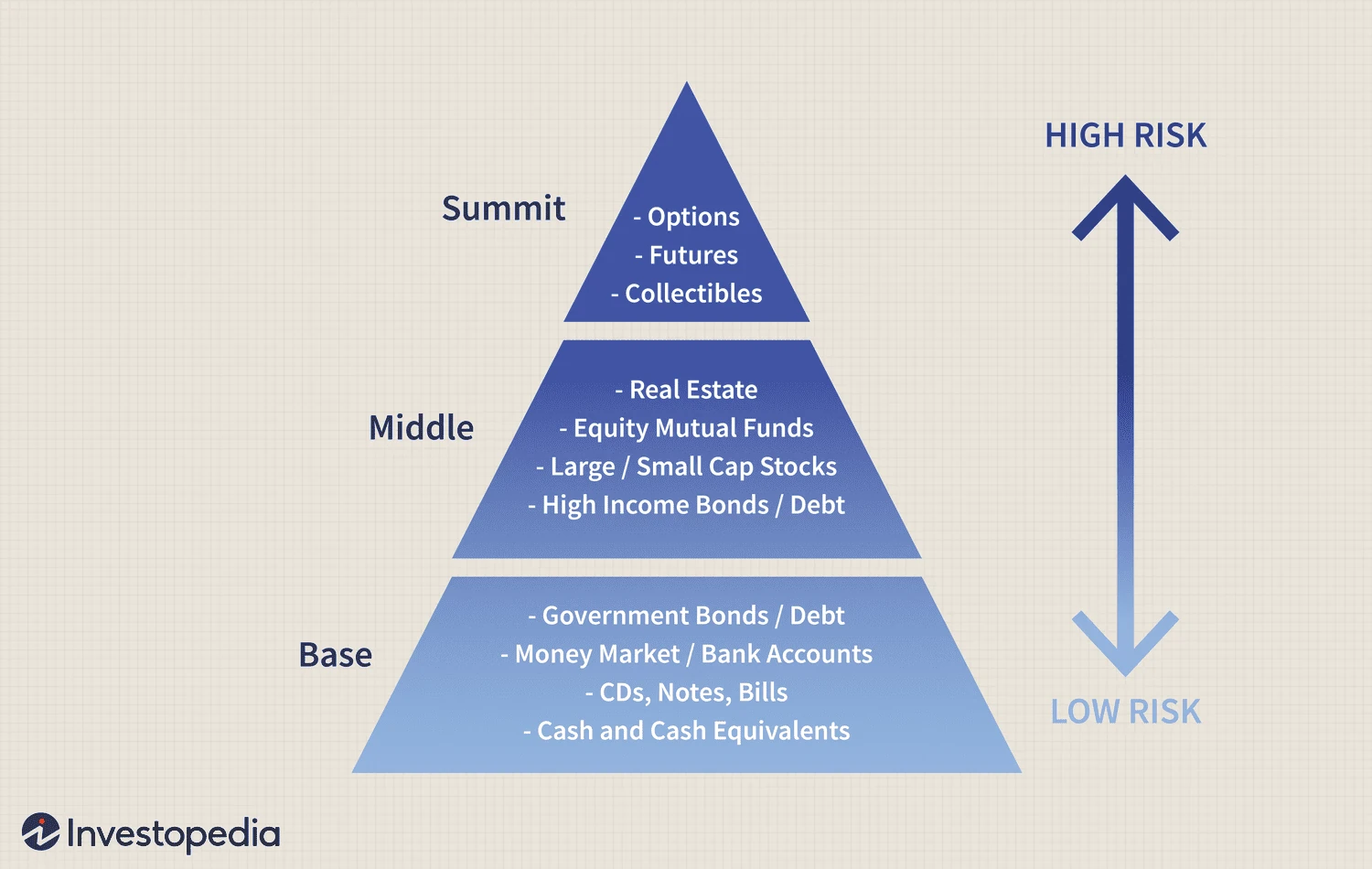

Cash or savings accounts: lowest risk, but lowest growth potential.
Bonds (government, corporate): moderate risk/reward.
Stocks (equities): higher risk, higher potential return.
Funds (mutual funds, ETFs): mix of assets; help beginners with built-in diversification.
Diversification and portfolio
He’s likely heard the phrase “don’t put all your eggs in one basket.” In investing, that means spreading risk across different asset types so his portfolio is less vulnerable to any single asset’s poor performance.
Time horizon & risk tolerance
Time horizon: how long he expects to keep the money invested. If he’s investing for 20-30 years (retirement, etc.), he may tolerate more risk.
Risk tolerance: his comfort with the possibility of losing value in the short term for potential long-term gain. These two asks determine how aggressive or conservative his strategy should be.
Fees, costs & expenses
Even as a beginner, he must know fees matter: higher fees reduce net returns over time. One site found the average person paid 0.75% in management fees, which over decades can hurt.
“Start with what you know” / “buy and hold” mindset
Instead of trying to chase hot tips or timing the market, many experts recommend starting simple: pick broad funds or index-oriented investments and hold for the long term.
3. Step-by-Step: How to Begin Investing with Little Money
Here’s a beginner-friendly roadmap: step-by-step investing for beginners.
Step 1 – Get your financial base in place
Pay off high-interest debt (e.g., credit cards) if present — because the interest you pay may exceed investment returns.
Build a small emergency fund (3-6 months of expenses) so you’re not forced to sell investments in a crisis.
Make sure basic living expenses are covered; investing is less useful if you’ll have to liquidate investments prematurely.
Step 2 – Set clear goals
What is he investing for? Retirement, buying a house, starting a business? Having clear goals helps define time horizon and strategy
Step 3 – Decide how much and how often to invest
Even with little money, consistency matters. For example, investing a small amount each month rather than trying to “get it perfect.
Avoid the trap of waiting for the “perfect time” — time in the market often beats trying to time the market.
Step 4 – Choose the investment vehicle
As a beginner, his choice likely falls into one (or more) of these:
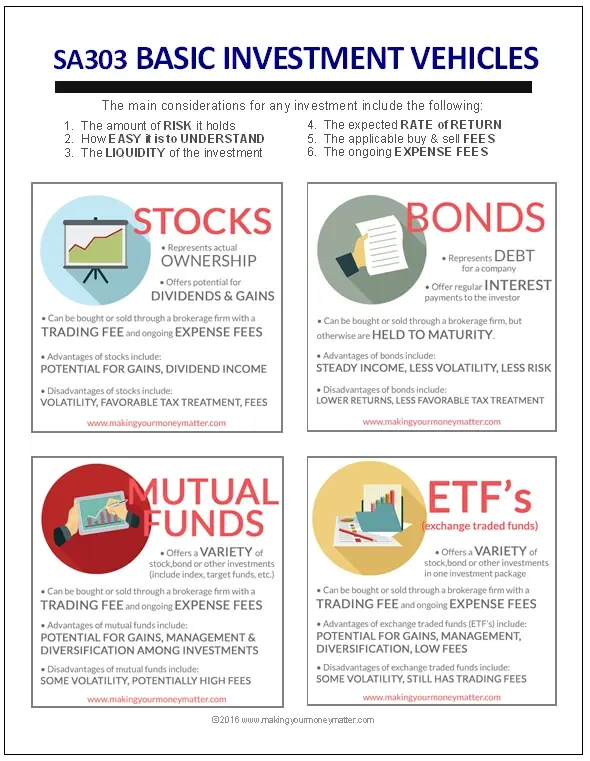
Index funds / ETFs: Broad, low-cost, and beginner-friendly.
Mutual funds: Pooled investments; good but watch minimums/fees.
Individual stocks: Possible, but riskier. Many beginners benefit more from starting with diversified funds.
Robo-advisors: Automated investment platforms; useful for beginners wanting a hands-off approach.
Step 5 – Build and monitor your portfolio
Allocate across asset classes as appropriate (stocks, bonds, maybe real-estate funds) depending on risk tolerance.
Periodically review but avoid constantly tweaking based on market noise.
Rebalance if one asset class drifts too far from your intended allocation.
Step 6 – Stay disciplined and keep learning
Invest on autopilot if possible (e.g., automatic monthly transfers).
Avoid emotional decisions (panic selling, chasing gains).
Continue educating yourself. Even seasoned investors learn continuously.
4. Beginner-Friendly Investment Strategies & Options
Here are some easy investment options for beginners, and strategies tailored to someone just starting.
Beginner-friendly vehicles
Low-cost index funds / ETFs: e.g., tracking the S&P 500 or total-market. Many experts say beginners should have the bulk of holdings here.
Target-date funds: Choose based on when he wants to retire; the fund automatically adjusts allocation over time.
Robo-advisors: If he wants minimal involvement, these provide automated diversification and rebalancing.
Fractional shares / micro-investing apps: If he’s investing with little money, these allow him to buy “a slice” of higher-priced stocks or funds.
Dollar-cost averaging (DCA): Investing fixed amounts regularly regardless of market levels — reduces timing risk.
Sample strategy for a beginner
Allocate maybe 80 % to a broad stock-market index fund (for growth) and 20 % to a bond fund (for stability) — adjust based on his risk tolerance and time horizon.
As he becomes more comfortable, he might add a small portion (say 5-10 %) into specific themes or individual stocks — but only once he understands them.
Use automatic monthly investment of whatever sum he’s comfortable with.
Avoid high-fee funds, high-risk “get rich quick” schemes, or trying to “time the market”.
Common pitfalls beginners should avoid
Trying to pick “winning” stocks early on instead of starting broad.
Paying high fees, which can erode returns significantly over decades.
Letting emotions drive decisions (selling in panic, buying in euphoria).
Neglecting emergency savings and carrying high‐interest debt.
5. Where to Start Today: Beginner Investing Checklist
Here’s a practical checklist he can follow over the next week or month to get started investing.
Review current finances (income, expenses, debt, savings).
Pay down or plan for any high‐interest debt (e.g., >6 %).
Set aside a small emergency fund (if not already).
Define one or two investing goals (e.g., retirement in 30 yrs, house in 10 yrs).
Choose how much he can comfortably invest monthly (even modest is fine).
Open an investment account (brokerage, robo-advisor, or fund provider) that offers low fees.
Select one or two beginner-friendly funds (e.g., broad index + bond fund).
Set up automatic monthly contributions.
Read short educational materials (guides by Fidelity Investments, Investopedia etc).
Commit to learning continuously and staying invested for the long term.
6. FAQs for Beginner Investors
Q: How little money can I start with?
A: A modest amount is fine — even $25‐50/month is meaningful when done consistently over many years.
Q: Should I wait for the “right time” to invest?
A: Trying to time the market is difficult, especially for beginners. A disciplined regular investment plan is often more reliable.
Q: How much risk should I take?
A: It depends on his time horizon and how comfortable he is with losing value in the short term. Longer horizon → can tolerate more risk. Shorter horizon → lean more conservative.
Q: What if I only invest now for a few years and then stop?
A: That’s okay, but investing for many years (ideally decades) gives compound growth time to work. The sooner he starts, the better.
Q: Can I just buy one stock?
A: Technically yes, but for beginners it’s safer to start with diversified investments (funds/ETFs) before picking individual stocks
7. The Bottom Line
Starting to invest doesn’t require a large sum of money, nor does he need to be an expert. What matters more is:
Start now (time is a powerful ally).
Invest consistently (even small amounts).
Keep it simple (broad funds, low fees).
Stay long term (ignore short-term noise).
By following these steps and maintaining a learner-mindset, he can build a strong foundation with beginner investing advice, beginner-friendly investment options, and a growing investment portfolio for beginners that evolves over time.
🏁 Conclusion
Starting an investment journey may seem intimidating at first, but every successful investor began exactly where you are — with curiosity, small steps, and commitment. The key takeaway for any beginner is simple: you don’t need a lot of money to start, but you do need to start early and stay consistent.
By following the beginner-friendly investment strategies discussed in this guide — setting clear goals, choosing low-cost diversified funds, and automating regular contributions — you can build a strong foundation for long-term financial growth. Remember, time in the market beats timing the market, and even small, steady investments can grow significantly through the power of compounding.
“The best time to plant a tree was 20 years ago. The second-best time is today.”
This saying perfectly applies to investing — the earlier you begin, the more rewarding your financial future becomes.
So start small, stay informed, and let your money work for you. Your future self will thank you. 🌱💰
📚 Sources & References
Below are the verified and up-to-date sources used throughout this guide on “Investing for Beginners: Where to Start”, gathered via real-time SERP analysis and reputable financial education platforms:
Rule One Investing – How to Invest Money: A Beginner’s Guide
🔗 https://www.ruleoneinvesting.com/blog/how-to-invest/how-to-invest-money-a-beginners-guide
Money with Katie – How to Confidently Start Investing: A Beginner’s Guide
🔗 https://moneywithkatie.com/blog/how-to-confidently-start-investing-a-beginners-guide
Fidelity Investments – Investing for Beginners: A Guide to Get Started
🔗 https://www.fidelity.com/learning-center/trading-investing/investing-for-beginners
Kiplinger – How to Start Investing in the Stock Market
🔗 https://www.kiplinger.com/investing/how-to-start-investing-in-the-stock-market
Empower (formerly Personal Capital) – How to Start Investing: A Beginner’s Guide
🔗 https://www.empower.com/the-currency/money/how-to-start-investing-beginners-guide
NerdWallet – How to Invest in Mutual Funds: Step-by-Step
🔗 https://www.nerdwallet.com/article/investing/how-to-invest-in-mutual-funds
Investopedia – Investing 101: How to Start Investing
🔗 https://www.investopedia.com/articles/basics/06/invest1000.asp
Investopedia – The 3 S’s of Simple Investing
🔗 https://www.investopedia.com/articles/basics/11/3-s-simple-investing.asp
SovereignBoss – Investing Statistics: How People Invest and What Works
🔗 https://sovereignboss.co.uk/investing-statistics
Morningstar – How to Build an Investment Portfolio
🔗 https://www.morningstar.com/lp/how-to-build-an-investment-portfolio








































